🌍 Environment – Scientific Framework in The Omega Instinct
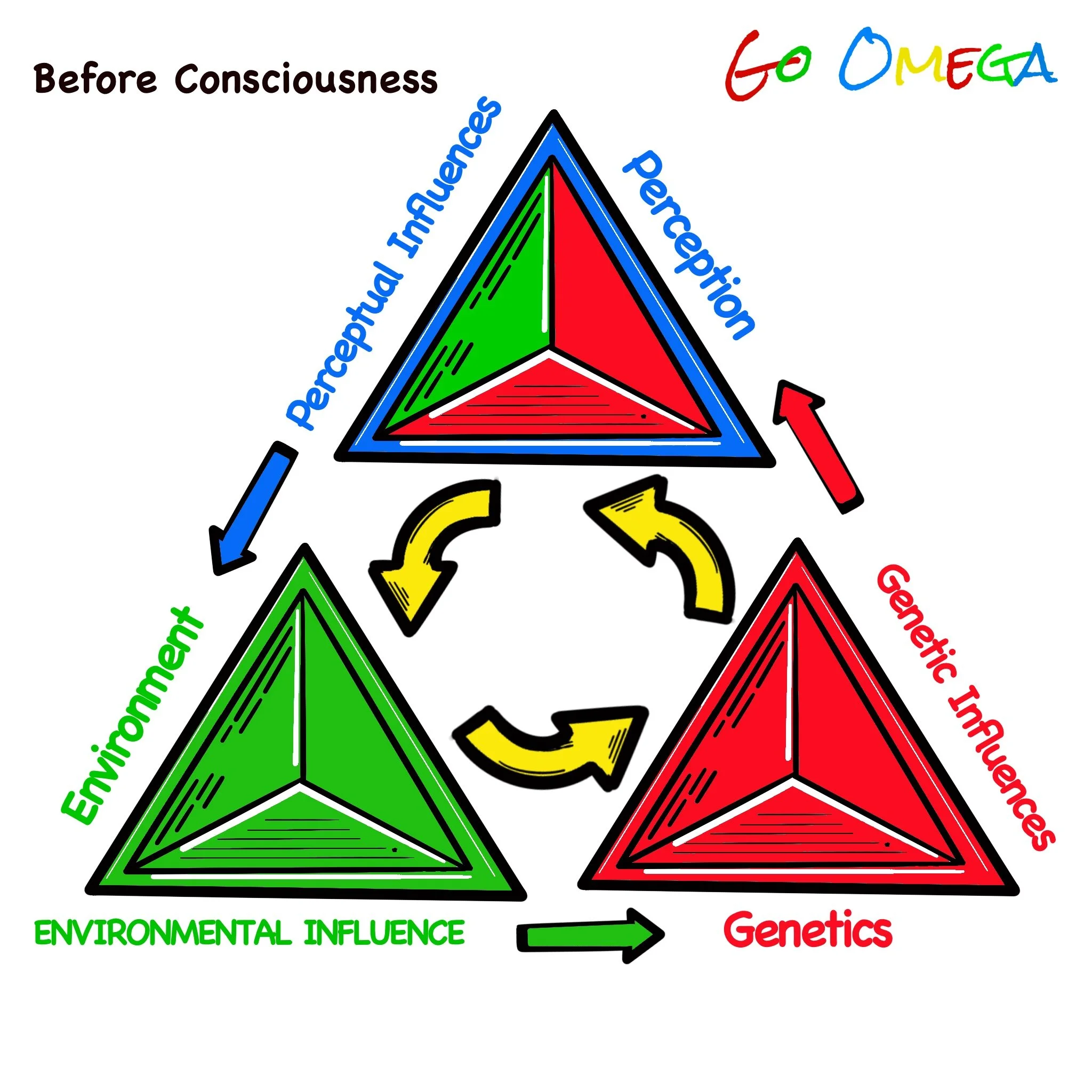
In The Omega Instinct, the environment refers to all external factors that influence the development, behavior, and functioning of the human organism. These factors interact with biological systems to shape the self across time.
Unlike genetics, which originates internally, environmental forces act upon the body and brain from the outside—but their effects are just as real, and often just as powerful.
🔬 Major Domains of the Environment
1. Physical Environment
Geography and climate: Terrain, altitude, weather, seasons, natural disasters
Toxins and pollutants: Air quality, heavy metals, chemicals, radiation
Pathogens: Exposure to viruses, bacteria, parasites, and disease vectors
Nutrition and resources: Availability of food, water, shelter
These factors influence everything from immune system development to brain structure, stress physiology, and sensory processing.
2. Social Environment
Family systems: Parenting style, attachment, safety, early bonding
Peers and relationships: Social learning, approval, rejection, modeling
Social hierarchy: Power dynamics, access to resources, perceived status
Social environments shape emotional regulation, behavior modeling, and identity formation. They can trigger chronic stress or prosocial development, depending on stability and support.
3. Cultural Environment
Language, religion, and tradition
Cultural Moral codes, values, and beliefs
Cultural attitudes toward behavior, emotion, authority, and the self
These factors influence moral reasoning, identity, and superego development (within the Omega framework). They also shape how behaviors are interpreted and reinforced.
4. Informational Environment
Media exposure: TV, internet, social media, music, books
Education systems: Curriculum, teaching style, access to knowledge
Narrative structures: Stories we are told about the world, others, and ourselves
Information environments influence cognitive framing, attention, motivation, and neural plasticity. Repeated exposure to ideas or imagery rewires perception and biases decision-making.